Google Drive in 2025 employs strong security features including encryption in transit and at rest, two-factor authentication (2FA), granular access controls, and continuous monitoring to protect user data. However, it does not provide default end-to-end encryption, meaning Google retains encryption keys and can access stored files if required. For enhanced privacy, client-side encryption or third-party tools are recommended. Google also integrates advanced data loss prevention (DLP) and threat detection features, especially for business users within Google Workspace, to help comply with regulatory requirements and prevent unauthorized data exposure.
Key security features and privacy aspects of Google Drive in 2025 include:
- Encryption in transit: Uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure data moving between devices and Google servers, protecting against interception.
- Encryption at rest: Files are encrypted on Google servers using AES-128 or AES-256 encryption standards, ensuring data confidentiality even if physical servers are compromised.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Adds an extra verification step beyond passwords to reduce unauthorized access risks.
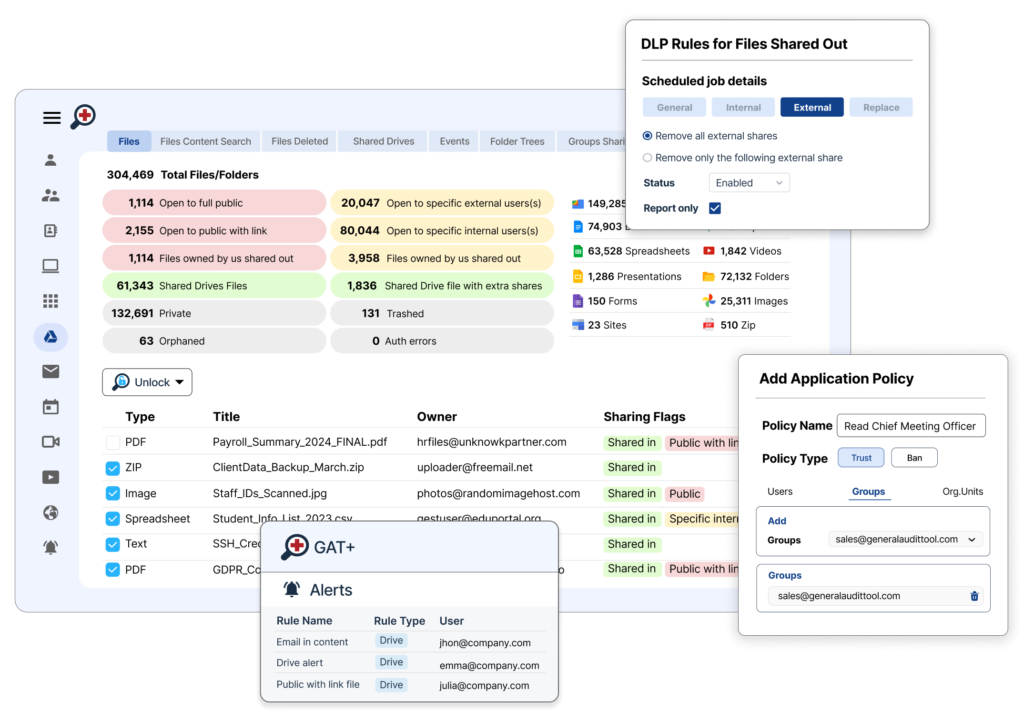
- Granular sharing controls: Users and admins can set detailed permissions for internal, external, or public sharing to minimize accidental oversharing.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Google Workspace offers DLP policies to detect and prevent sensitive data leaks, with third-party integrations like Material Security enhancing visibility and remediation.
- Audit logs and monitoring: Google Workspace provides audit trails for file access and sharing activities, aiding compliance and security oversight.
- Privacy limitations: Google retains encryption keys and scans data for service improvement and compliance, meaning user data is not fully private from Google employees or authorities. This lack of zero-knowledge encryption means sensitive data stored on Drive carries privacy risks.
- Phishing and social engineering risks: Despite technical protections, human factors remain a major vulnerability, especially with increasingly sophisticated AI-generated phishing attacks.
- Disabling less secure apps: Since May 2025, Google Workspace no longer supports less secure third-party apps, improving account security.
- Generative AI privacy commitments: Google Workspace maintains robust privacy policies to protect user data in AI-powered features.
For organizations and individuals handling highly sensitive or regulated data, it is advisable to use client-side encryption tools or additional security layers beyond Google Drive’s native protections to ensure privacy and compliance.
In summary, Google Drive in 2025 offers robust security infrastructure and administrative controls suitable for most users and businesses, but users should be aware of privacy trade-offs and consider supplementary encryption for highly sensitive data.