Site speed and HTTPS both play important roles in Google indexing and ranking, with site speed directly affecting crawl efficiency and user experience, and HTTPS serving as a confirmed but relatively lightweight ranking signal that enhances security and trust.
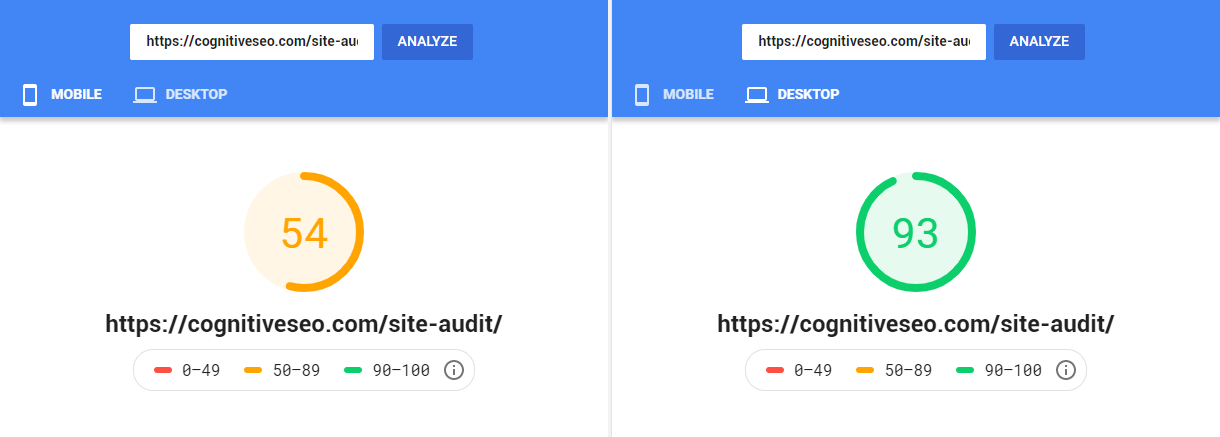
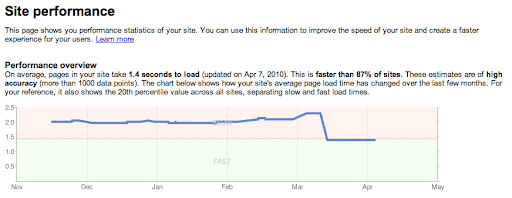
Google prioritizes fast-loading websites because slow pages can reduce crawl frequency and indexing speed, as Googlebot has limited crawl resources and may abandon slow or unresponsive sites. Site speed is a direct ranking factor included in Google’s algorithm, notably through Core Web Vitals metrics, which measure user experience aspects like loading speed and interactivity. Faster sites improve user engagement and reduce bounce rates, which indirectly supports better rankings.
HTTPS is a confirmed ranking factor that Google uses to promote secure browsing. Websites with HTTPS benefit from a small ranking boost, increased user trust, elimination of “Not Secure” warnings, and better referral data preservation. While HTTPS itself does not guarantee faster indexing, secure sites tend to load faster and more reliably, which helps Googlebot crawl and index them more effectively. Sites with SSL errors or expired certificates may be skipped or penalized in crawl depth.
In summary:
| Factor | Role in Google Indexing & Ranking | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Site Speed | Direct ranking factor; affects crawl rate and indexing speed | Slow sites get crawled less frequently; Core Web Vitals measure speed and user experience |
| HTTPS | Confirmed ranking signal; improves trust and security | Small ranking boost; prevents security warnings; can improve crawl reliability and user trust |
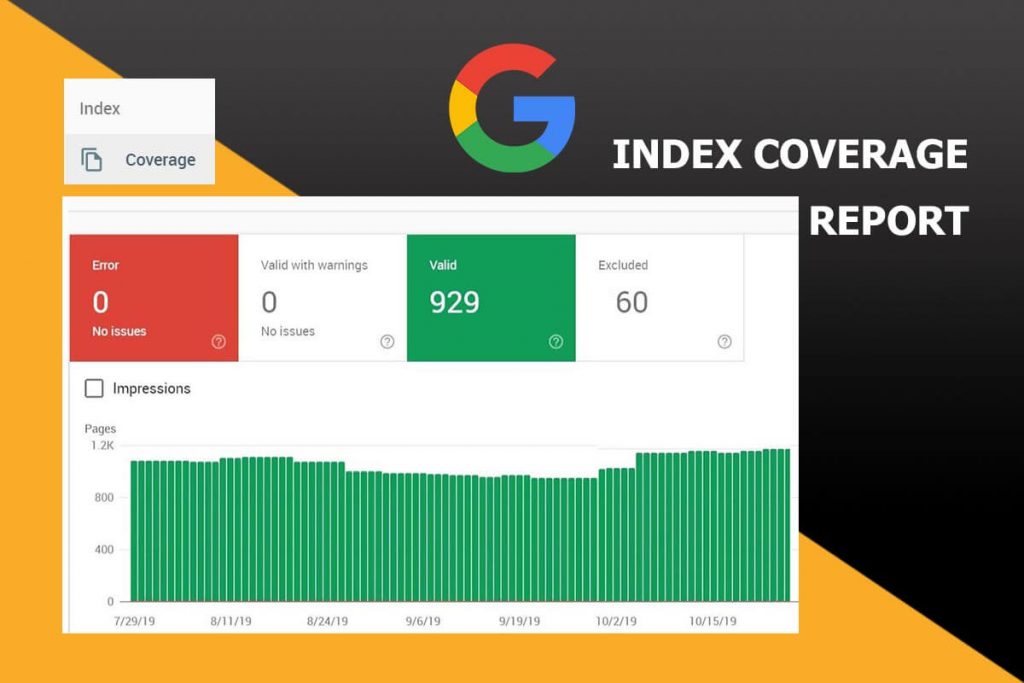
Google Search Console can be used to monitor HTTPS performance, security issues, and Core Web Vitals to optimize indexing and ranking. Maintaining a fast, secure, and well-structured website is essential for maximizing Google indexing efficiency and SEO performance.
References: