Overview of Google’s Search Process
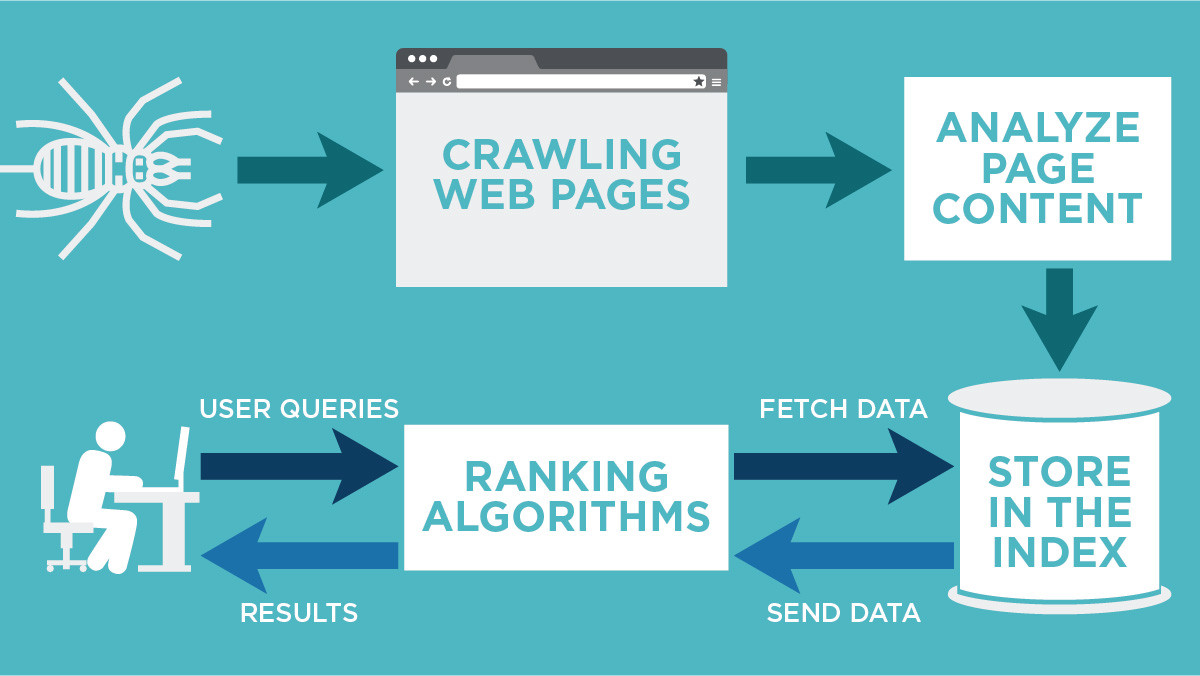
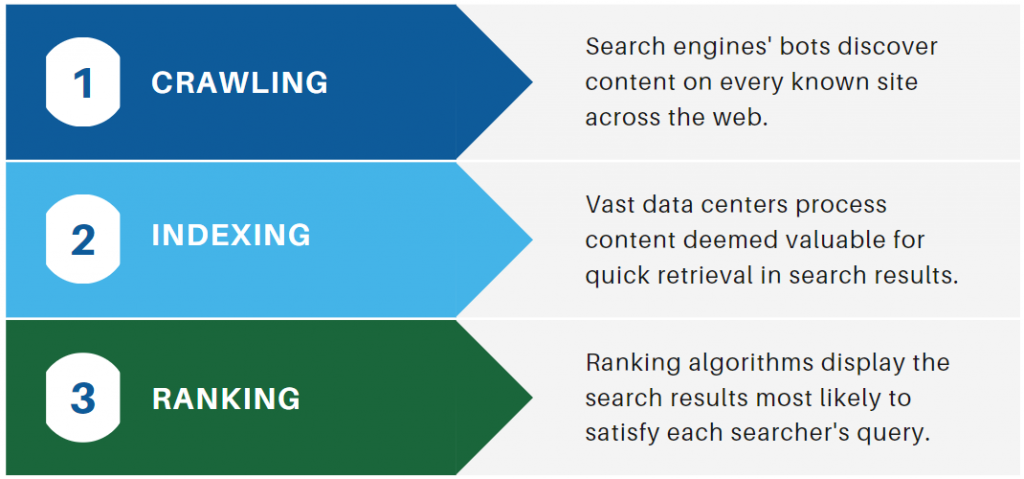
Google’s ability to deliver relevant search results relies on three core processes: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Each step is automated, complex, and interdependent, ensuring that the search engine can efficiently organize and serve the vast amount of content on the web.
Crawling
Crawling is the discovery phase where Google’s automated bots (often called “spiders” or “crawlers”) systematically browse the web to find new and updated content. These crawlers follow links from page to page, obeying directives in files like robots.txt, and can discover various content types, including web pages, images, videos, and PDFs. The goal is to keep the search index as current as possible by continuously scanning for fresh or modified content.
Key Points:
- Crawlability: A page must be accessible to crawlers (not blocked by robots.txt or server errors) to be discovered.
- Crawl Budget: Google allocates a limited amount of crawling resources to each site, so site structure and internal linking influence how much content gets crawled.
- Sitemaps: Webmasters can submit sitemaps to help Google discover important pages more efficiently.
Indexing
After a page is crawled, indexing is the process by which Google analyzes, understands, and stores the page’s content in its massive index database. During indexing, Google parses the HTML, executes JavaScript, and renders the page to understand its structure and content. It also evaluates metadata, such as title tags and alt attributes, to better comprehend the page’s subject matter.
Duplicate Content and Canonicalization:
Google groups similar pages and selects a “canonical” version to represent the content in search results, reducing duplicate content issues. Other versions may be shown in specific contexts (e.g., mobile users), but the canonical is prioritized.
Indexability:
Not all crawled pages are indexed. Factors affecting indexability include content quality, technical errors, meta tags (like noindex), and site architecture. If a page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results.
Ranking
Ranking determines the order in which indexed pages appear in response to a user’s query. Google uses hundreds of signals—including relevance, content quality, user experience, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and backlinks—to decide which pages best answer the query. The ranking algorithm is dynamic and personalized, considering factors like location, device, and search history to deliver the most relevant results.
Key Points:
- Relevance: The content must closely match the user’s intent and query.
- Quality: High-quality, original, and well-structured content ranks better.
- User Signals: Metrics like click-through rate and dwell time may influence rankings over time.
Serving Results
Once the ranking is complete, Google assembles and displays the results on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP), often enriched with features like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and local packs, depending on the query.
Summary Table
| Process | Purpose | Key Activities | Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crawling | Discover new/updated content | Follow links, parse robots.txt, read sitemaps | Site accessibility, crawl budget |
| Indexing | Analyze, understand, and store content | Parse HTML/JS, select canonical, filter quality | Content quality, technical errors |
| Ranking | Order results by relevance and quality | Apply ranking signals, personalize results | Relevance, quality, user signals |
Technical SEO Considerations
- Ensure crawlability: Fix broken links, use a logical site structure, and avoid blocking crawlers unnecessarily.
- Optimize for indexability: Use clear, unique content; fix technical errors; and specify canonical URLs when appropriate.
- Improve ranking factors: Focus on content quality, user experience, and authoritative backlinks.
Conclusion
Google’s crawling, indexing, and ranking processes are foundational to how search engines organize and deliver information. Understanding these mechanisms helps webmasters and SEO professionals optimize their sites for better visibility and performance in search results.