The Five Main UTM Parameters Explained
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters are short text codes added to URLs to help marketers track the effectiveness of online campaigns and understand where their website traffic originates. These parameters are widely used in analytics platforms like Google Analytics to segment and analyze traffic sources, mediums, campaigns, and more. Below is a detailed explanation of the five main UTM parameters: Source, Medium, Campaign, Term, and Content.
| Parameter | Purpose | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| utm_source | Identifies the origin of the traffic | facebook, google, newsletter |
| utm_medium | Specifies the marketing channel or medium | email, cpc, social |
| utm_campaign | Names the specific campaign or promotion | summer_sale, product_launch |
| utm_term | (Optional) Tracks paid keywords or targeting terms | running_shoes, nyc_events |
| utm_content | (Optional) Differentiates between similar ads or links in the campaign | banner_ad, text_link |
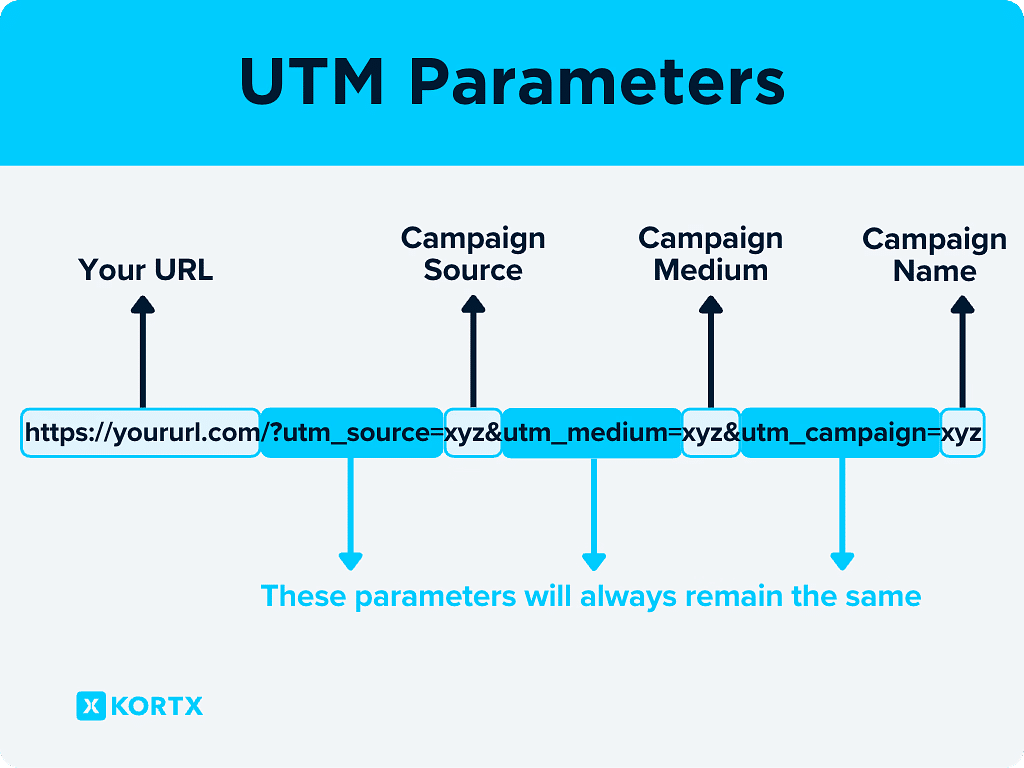
Source (utm_source)
The utm_source parameter identifies the specific site, platform, or entity sending traffic to your website. It answers the question: Where did the visitor come from? Common examples include “facebook” for traffic from Facebook, “google” for organic search traffic from Google, or “newsletter” for email campaigns. This parameter is essential for distinguishing between different traffic sources and understanding which are most effective.
Medium (utm_medium)
The utm_medium parameter describes the general category of the marketing channel. It answers: How did the visitor get here? Typical values are “email” for email marketing, “cpc” (cost-per-click) for paid search ads, “social” for social media, and “organic” for non-paid search traffic. This helps marketers compare the performance of different channels (e.g., email vs. social media).
Campaign (utm_campaign)
The utm_campaign parameter names the specific marketing campaign, promotion, or initiative. It answers: Which campaign does this traffic belong to? Examples include “summer_sale,” “holiday_discount,” or “webinar_signup”. This allows for granular analysis of campaign effectiveness and ROI.
Term (utm_term)
The utm_term parameter is optional and primarily used in paid search campaigns to track the specific keyword or targeting term that triggered the ad. It answers: Which keyword or term brought this traffic? For example, “running_shoes” or “best_laptop_deals”. This is especially useful for optimizing paid search campaigns.
Content (utm_content)
The utm_content parameter is also optional and used to differentiate between multiple links or creatives within the same campaign. It answers: Which specific link or ad creative was clicked? For instance, “banner_ad” vs. “text_link” or “video_ad” vs. “image_ad”. This helps in A/B testing and optimizing ad creatives.
How UTM Parameters Are Used
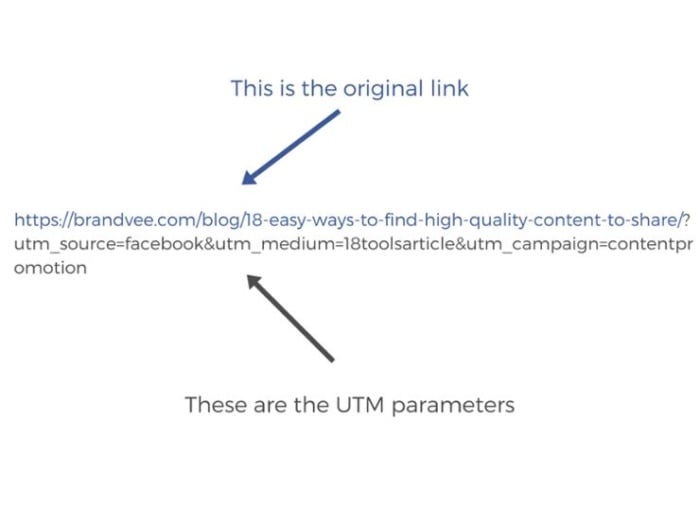
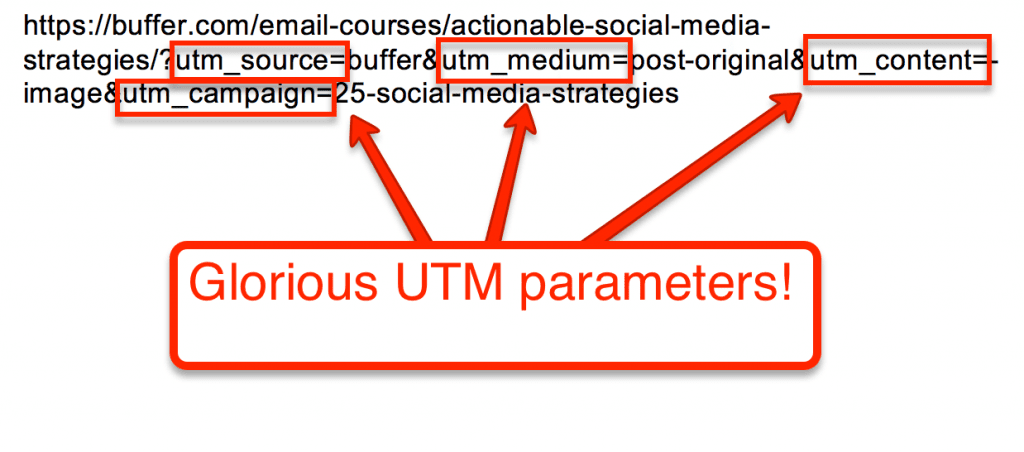
UTM parameters are appended to the end of a URL, following a question mark (?), and separated by ampersands (&). For example:
https://example.com/?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=summer_sale&utm_term=discount&utm_content=banner_ad
This URL tells analytics tools that the visitor came from a newsletter (source), via email (medium), as part of the “summer_sale” campaign, clicked on a link targeting the “discount” term, and interacted with a “banner_ad” creative.
Summary
- utm_source: Identifies the traffic source (e.g., facebook, google).
- utm_medium: Specifies the marketing channel (e.g., email, cpc, social).
- utm_campaign: Names the campaign (e.g., summer_sale, product_launch).
- utm_term: (Optional) Tracks the keyword or targeting term.
- utm_content: (Optional) Differentiates between ad creatives or links.
These parameters provide marketers with actionable data to measure, compare, and optimize their digital marketing efforts.