Securing a WordPress database involves several key strategies, including using custom prefixes and restricting user privileges. Here's how you can implement these measures:
Custom Database Prefixes
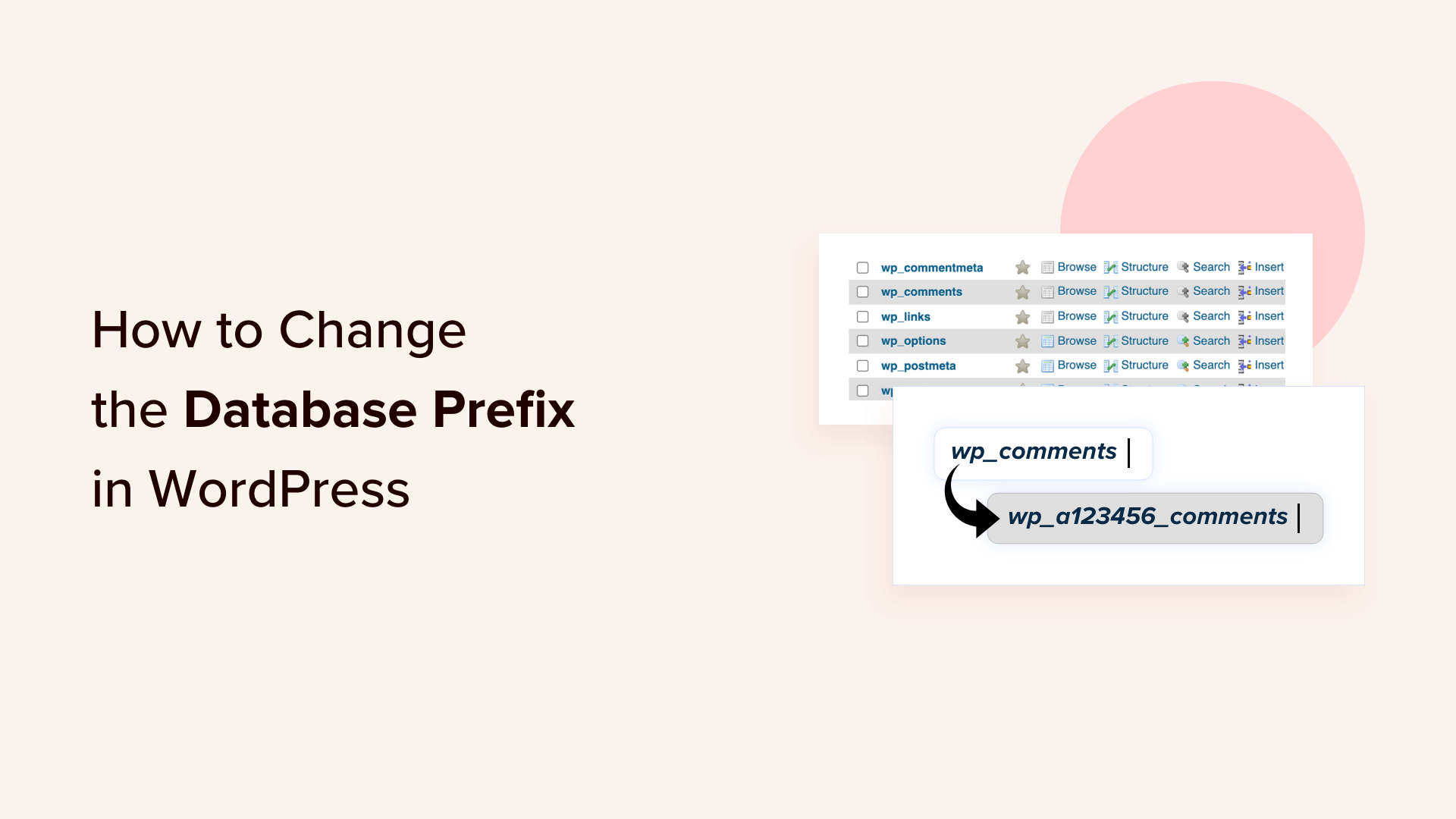
Why Change the Prefix?
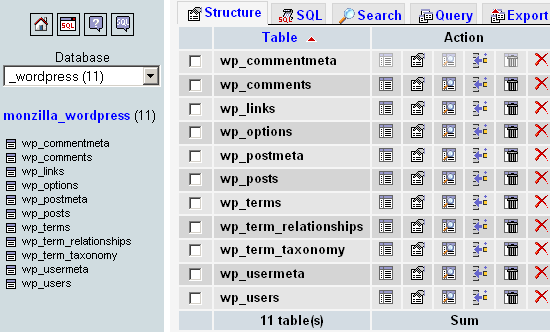
- Security by Obscurity: Changing the default
wp_prefix makes it harder for attackers to guess table names, which can help prevent SQL injection attacks. - Limitation: This is not a foolproof security measure but can be part of a broader security strategy.
How to Change the Prefix
- During Installation: You can set a custom prefix during the WordPress installation process.
- After Installation: Use SQL queries to replace all instances of the default prefix with your custom one. This requires careful execution to avoid breaking your site.
Restricting User Privileges
Why Limit Privileges?
- Damage Control: If an attacker gains access to your database credentials, limited privileges can restrict the damage they can do.
- Compliance: Limiting user privileges is essential for complying with data protection regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS.
How to Limit Privileges
- Create a New User: Create a dedicated MySQL user for your WordPress site.
- Assign Limited Privileges: Grant only necessary privileges like
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETEto this user. - Update WordPress Configuration: Update your
wp-config.phpfile to use the new user credentials.
Example SQL Commands
-- Create a new user
CREATE USER 'wpuser_secure'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPasswordHere';
-- Grant limited privileges
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON your_database_name.* TO 'wpuser_secure'@'localhost';
Best Practices Summary
- Regular Updates: Keep WordPress, themes, and plugins updated.
- Unique Credentials: Use strong, unique usernames and passwords.
- Limit Login Attempts: Implement measures to limit login attempts.
- Use Security Plugins: Consider using security plugins for additional protection.